Understanding the Kivy Framework
Subject: Mobile Application Development (VU-CSS 223)Kivy is an open-source Python library for building cross-platform applications (Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS). It focuses on natural user interfaces (NUIs) such as multitouch, gestures, and modern UI components.
Kivy provides:
- A rich set of widgets (buttons, labels, text inputs, layouts).
- Graphics engine built on OpenGL ES 2.0 for smooth rendering.
- Input handling for touch, mouse, keyboard, and sensors.
- It is especially popular for mobile apps, interactive tools, and rapid prototyping
Installing Kivy
First check if Kivy is installed on your system, open your terminal or command prompt and type
pip show kivyInstall Kivy Using pipM
pip install kivyFirst Kivy Application
Create a folder myapp, and create a python file e.g main.py and let it contain the code below
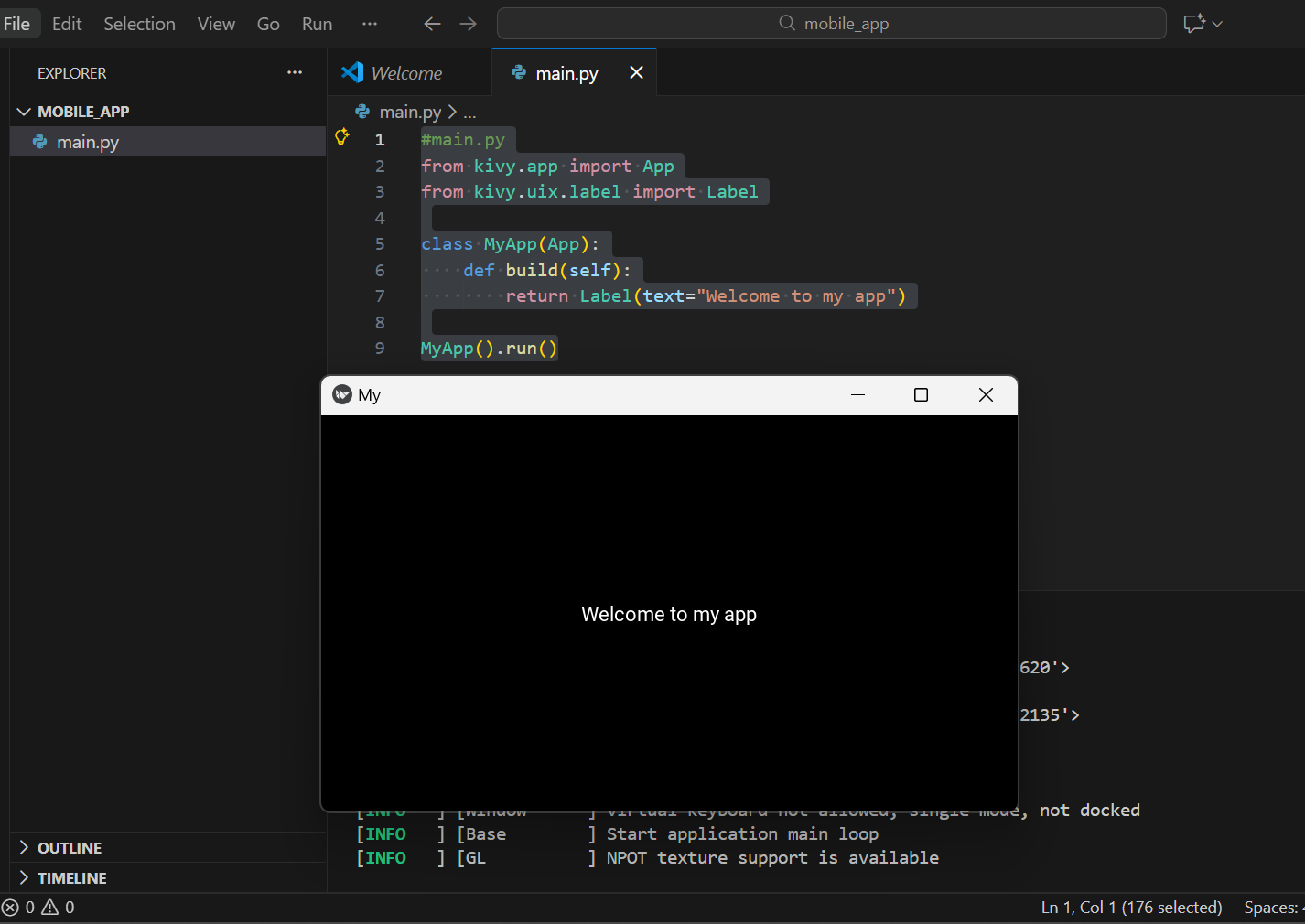
#main.py
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.label import Label
class MyApp(App):
def build(self):
return Label(text="Welcome to my app")
MyApp().run()
This program is a very small Kivy application. Kivy is a Python framework used to build mobile and desktop apps.
Let's break the code down:
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.label import Label
This imports two important things:
- App: the main class you use to create a Kivy application.
- Label: a widget that displays text on the screen.
class MyApp(App):
def build(self):
return Label(text="Welcome to my app")
Here we create a class MyApp, which is our application, that inherits from the App class. The build() function tells Kivy what should appear on the screen, in this case, we return a Label with the text "Welcome to my app". So when the app runs, it will simply show this text on the screen.
MyApp().run()
This line actually starts the application. It creates an object of MyApp and runs it.
By: Vision University
Comments
Favour Goodnews (learner)Date commented: 10-Dec-2025 07:38:13pm
I installed kivy and run it
Login to comment or ask question on this topic
Previous Topic Next Topic
- 1 Introduction to Mobile Application Development
- 2 Understanding the Kivy Framework
- 3 Kivy Widget: Label, Button
- 4 Introducing the KV Language
- 5 Layouts in Kivy
- 6 Event Handling and User Interaction